CyclicalEncoding
This package provides a function for encoding cyclic variables into two continuous variables using the sine and cosine functions. This encoding is useful for machine learning models that need to capture cyclical patterns in the data.
Installation
To install this package, run the following command in the Julia REPL:
using Pkg
Pkg.add("CyclicalEncoding")
Usage
To use this package, first import the cyclical_encode function:
using CyclicalEncoding
x = 5
min = 0
max = 10
sin_val, cos_val = cyclical_encode(x, min, max)
The cyclical_encode function tanks three arguments:
- The number to encode;
- The minimum value of the range;
- The maximum value of the range;
It returns a tuple containing the sine and cosine values of the encoded number.
How does a cyclical encoding works?
Sine and cosine functions are commonly used for encoding cyclical variables because they are periodic functions that repeat themselves after a certain interval. This makes them ideal for encoding variables that have a cyclical nature, such as time of day, day of the week, or month of the year.
When encoding a cyclical variable, we want to represent it as a point on a circle, where the angle of the point corresponds to the value of the variable. We can use the sine and cosine functions to calculate the x and y coordinates of the point on the circle, respectively.
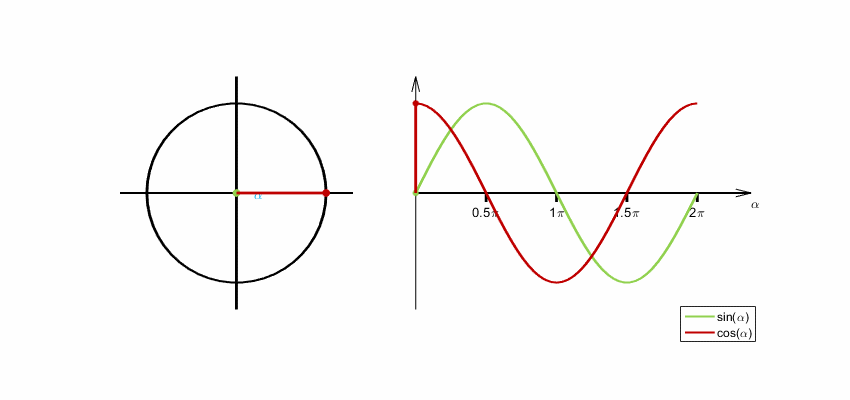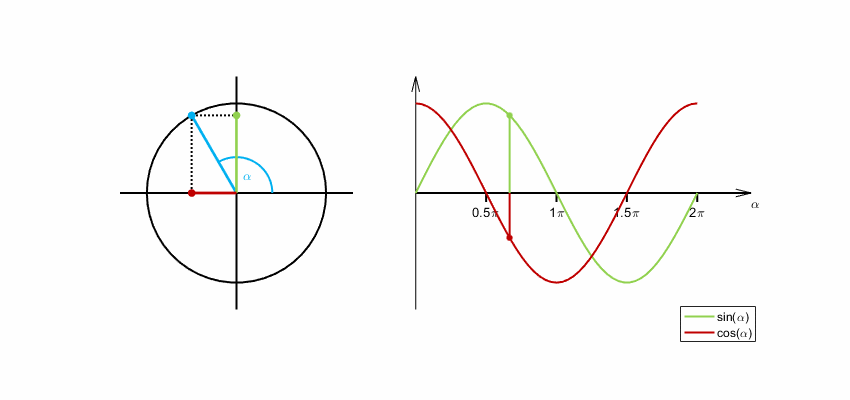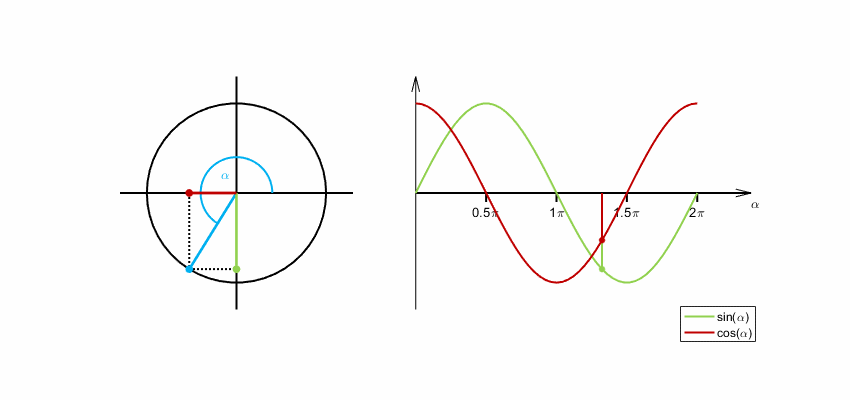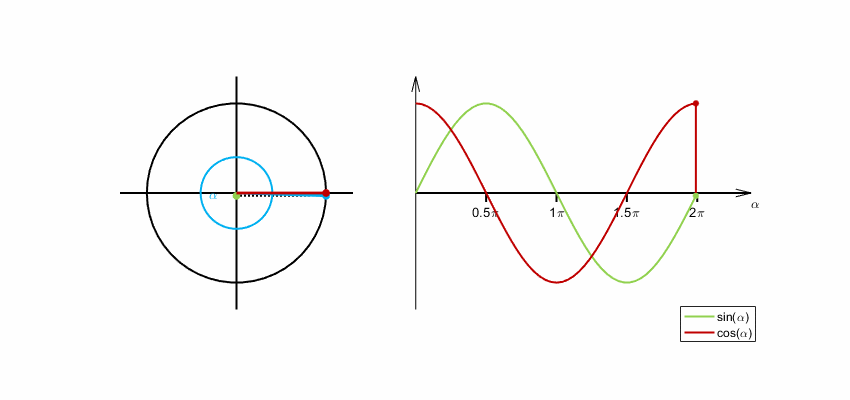
Eltos, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
By encoding a cyclical variable using sine and cosine functions, we can represent it as a point on a circle, which can be useful for visualization and analysis purposes. Additionally, the use of sine and cosine functions ensures that the encoding is periodic and wraps around smoothly, which can be important for certain applications.
Contributing
Contributions to this package are welcome! If you find a bug or want to suggest a new feature, please open an issue on the GitHub repository. If you want to contribute code, please fork the repository and submit a pull request.
License
This package is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.